
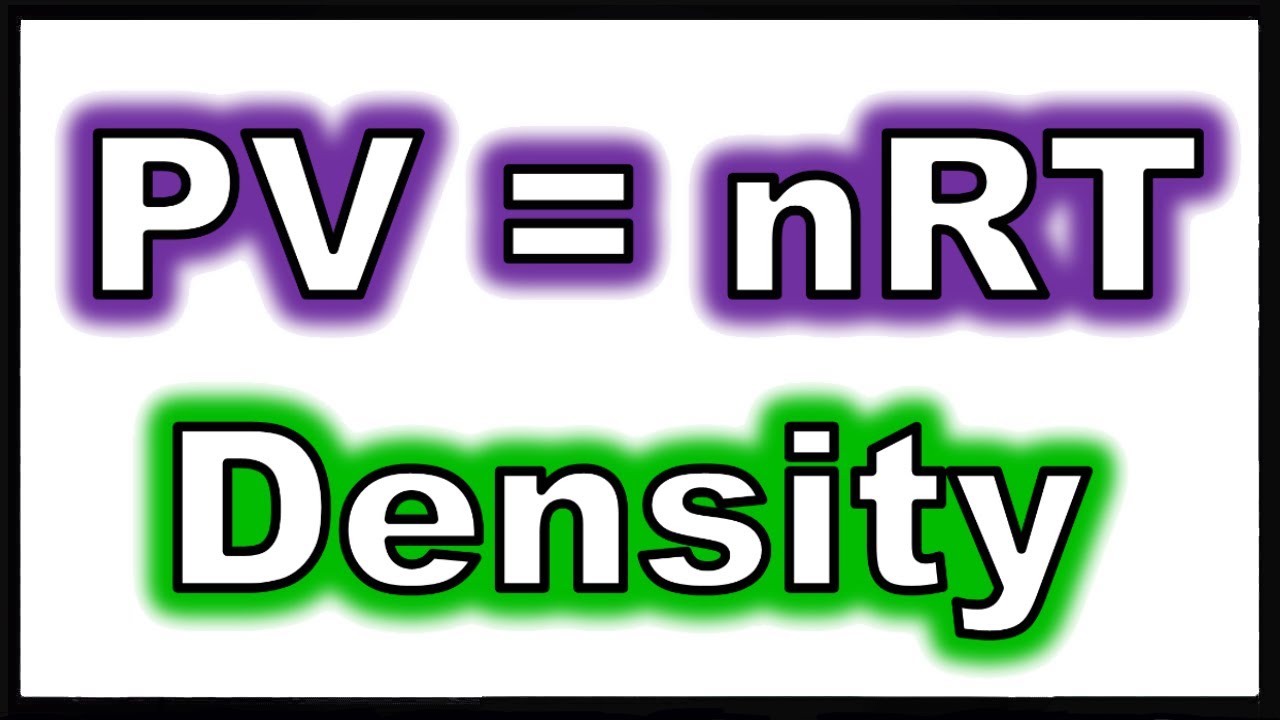
Sometimes you then have to convert number of moles to grams.
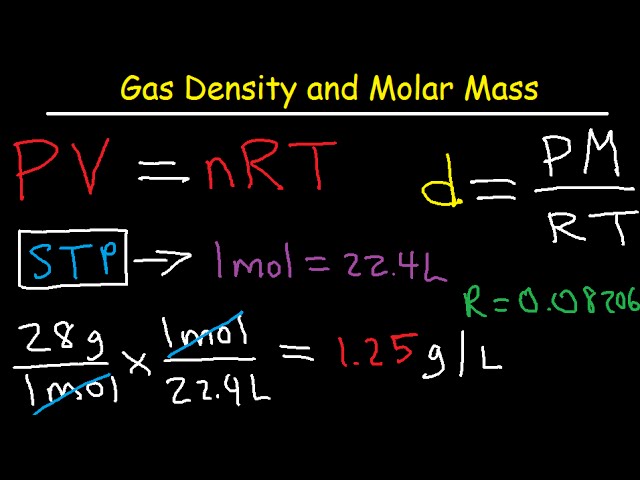
… The ideal gas law is PV = nRT, so if you know enough values, you can calculate volume (V) or the number of moles (n). What is density in PV nRT?ĭensity is defined as mass per unit volume. This means that for air, you can use the value R = 287 J/kg The value of R depends on the units involved, but is usually stated with S.I.
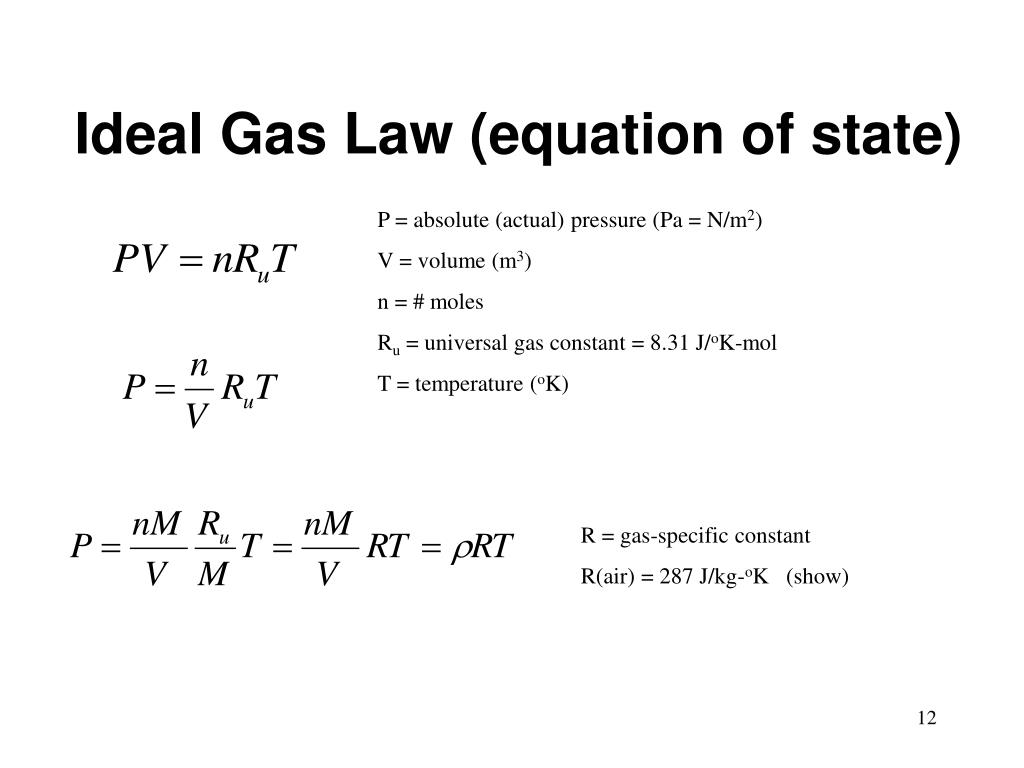
The ideal gas law is: pV = nRT, where n is the number of moles, and R is universal gas constant. We shall learn how to calculate the total energy and other properties, and apply this to electrons, phonons, photons, liquid helium, etc. How do you find the value of R in PV nRT? Ideal Gas Kai Hock 2013 - 2014 University of Liverpool Density of States 1 A particle in a 3-D box In an ideal gas, we assume that there is little interaction between atoms. But density is m/V, so flip the equation over to get: m/V = (MMP)/(RT) = density of the gas. To find this, remember the relationship between number of moles and mass. We know everything we need to find the volume now except the number of moles of gas. The original ideal gas law uses the formula PV = nRT, the density version of the ideal gas law is PM = dRT, where P is pressure measured in atmospheres (atm), T is temperature measured in kelvin (K), R is the ideal gas law constant 0.0821 atm(L)mol(K) just as in the original formula, but M is now the molar mass ( gmol … How do I find the density of a gas?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
